Home / Course Design / Assessment
Step 2: Assessment
Not every learning objective carries the same weight, how do you ensure your assessments are valid and reliable?
On this page you will find information about the basics of assessment in interdisciplinary education. As with all student-centred approaches, it is integral that educators ensure their range of assessments (exams, projects, orals, etc.) are, among other things, effective (format galvanises learning), valid (measuring what it is supposed to measured), reliable (meaningful and of high quality), transparent (students know what to expect) and feasible (practicality factors).
Foundations of Assessment
We intend to inform you of the various considerations that are prevalent for interdisciplinary education, however, there are some fundamental pedagogical terms and theories that should be known before educators embark on the complicated process of assessing student learning. For example, knowledge on constructive alignment, validity, reliability, etc. This site, presupposes that visitors at least have a basic knowledge of these theories.
If you do not possess this basic knowledge of assessment, that is okay; we can help! Below you can some sites that have been carefully selected to enlighten you on the important topics of quality of assessment, types of assessment, alignment, etc.
- The Centre of Expertise in Teaching and Learning (CELT) offers a plethora of resources for you to start your own education on the basics on the topic of assessment.
- Radboud University’s site provides a comprehensive and logical learning locale that is both informative and concise.
- CMU illustrates the importance of alignment with in your course.
Planning and Auditing for Quality
After you have carefully established your interdisciplinary learning objectives, the next step is to plan your total assessment package. Using an assessment scheme in your planning, will help to summarise the various assessments, their weightings and other important information. This is especially important when there there are multiple assessment opportunities within the course; filling out an assessment scheme visualises the various forms of assessment and serves as a check to ensure important learning areas are indeed prioritised and others are not neglected.
You can download an example frame of an assessment scheme, create your own and use it to plan how your learning objectives will be covered in each assessment, as well as to check if the weightings you allocate to each, are appropriate.
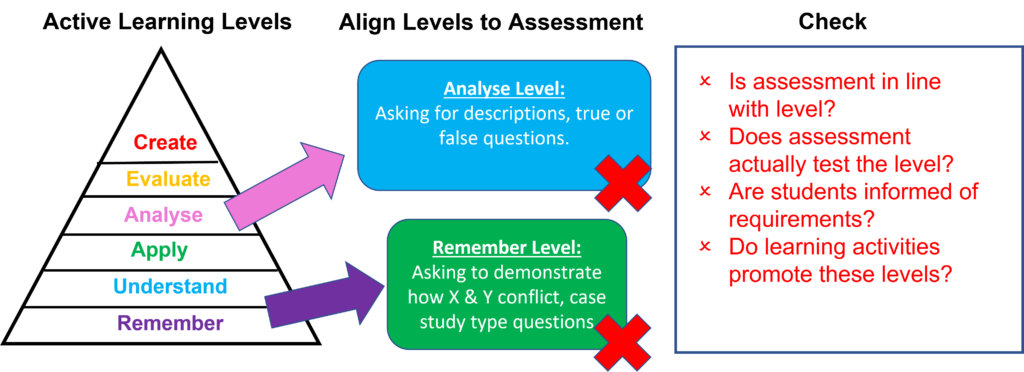
Do you always check to see if the levels at which you planned your students to learn, are indeed facilitated and assessed at those levels?
Sometimes, teachers can set assessments without consciously considering whether the Bloom’s (active learning) level they set in the learning objective, is tested in a valid manner. Let us look at some examples below.
The teacher considers the various Bloom’s taxonomy levels of the course’s learning objectives when deciding upon the assessment. For example, if students are required to ‘evaluate’, a high stakes case study assignment will be appropriate; if they are required to ‘identify’, a multiple-choice assessment will be adequate.

(N.B. the learning activity must be conducive to students practising these levels, in order to be able to prove their competence in the assessment.)
Teacher pays no attention to the learning objectives nor the Bloom’s taxonomy levels defining them. Rather, they set the assessment according to the content that was covered, not specifically to which level students need to prove their competence. There may be misalignment in the assessment as students are asked to prove their competence in a format or level that could be above or below the course’s intentions and how the level at which they were facilitated to learn.
Scrutiny of each Assessment
In order to clearly link learning objectives to each individual assessment and their questions, an assessment specification matrix could be used. These help to ensure you cover your learning objectives according to the desired weightings and help you to systematically check whether the Bloom’s taxonomy levels are appropriate and aligned for each question. As it clearly highlights the weightings of the different levels of learning objectives, important criteria are ensured to be allocated the suitable proportion of points, and the lower levels too.
Steps of the Assessment Specification Matrix
Column 1
From the assessment scheme, list the relevant L.O.s that go with this particular assessment.
Column 2
Specify in which form(s) each L.O. will be tested (e.g. multiple choice, open question, project, presentation, etc.)
Column 3
Specify at which Bloom’s taxonomy level each L.O. will be tested.
Column 4
Determine the appropriate weighting (in percentages) of each individual L.O. (how heavily they will feature in the overall exam), and fill out the percentages in the final column.
Column 5
Based on the weighting factor, determine the number of questions and the corresponding number of points to be awarded for each L.O.
Column 6
List relevant materials associated with this L.O.
Column 7
List which questions* from the assessment belonging to this L.O.
*List each question in full, check whether the question’s level is at same Bloom’s taxonomy level as original learning objective.
If you want a clear and organised manner to ensure your assessments are on the planned Bloom’s level and have the appropriate weightings, download the above matrix and carefully follow the steps to ensure validity in all of your assessments. Once you have completed the table, step back and double check if what you set out to assess, really is being assessed. Also, take another look at your weightings – do you need to adjust them so that the harder levels get a bigger share of the points?
Analysis of (each) Assessment
Performing an analysis of your assessment, is a quality check after the process is completed. It helps educators to identify weak areas that may indicate a low quality question, poor instruction/facilitation of a learning goal or problem areas in general.
For further detailed instructions on how to analyse your assessments, please refer to the step-by step guide, collated by the Behavioural & Management Sciences faculty at the University of Twente.
For open-ended questions: review questions with exceedingly high or low average scores, and any peculiar or highly common mistakes or misconceptions that may come to your attention while marking the exams or assignments.
For multiple choice exams: psychometric data of the entire exam as a whole and for each individual question.
Practical Assessment Rubrics to get you started...
Are you feeling unsure on how to practically assess certain aspects of your interdisciplinary course?
Assessing the individual in a group project is challenging; social loafing is real concern and a frequent complaint among student working in teams. Although peer review goes some way towards deterring these occurrences; they too have validity and reliability issues, where self-rating can skew an outcome or bias in the form of the ‘halo effect’ or reciprocity – can influence fair outcomes. Here, we have created an accountability rubric inspired by the Segmented Manager Method from Dommeyer, C. J. (2012).
We recommend you edit this rubric and adjust it to suit your particular needs. It can be used by tutors or peers.